Pre-Fertilization Structures and Events
Pre-Fertilization Structures and Events: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Structure of Flower, Filament of Stamen, Anther, Microsporangium, Tapetum, Endothecium, Microsporogenesis, Pollen Grain, Sporopollenin, Intine, Germ Pore, Exine, Economic Importance of Pollen Grain, etc.
Important Questions on Pre-Fertilization Structures and Events
In the given figure of embryo sac, choose the option that is correctly showing the parts (1), (2), (3) and (4).
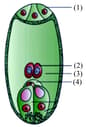
Which of the following represents the persistant remains of nucellus ?
Match the following:
| Column-I | Column-II | ||
| (a) | Coleorhiza | (i) | Birth cord |
| (b) | Umbilical cord | (ii) | The outer wall of a spore or pollen grain |
| (c) | Germ pores | (iii) | A sheath protecting the root of a germinating grass or cereal grain |
The process of development of pollen mother cell into a mature pollen grain includes:
The megaspores are formed from megaspore mother cell that are produced in which of the following region of ovule:
Pollen grains are able to withstand extremes of temperature and dessication because their exine is composed of
Assertion : If pollen mother cells has 42 chromosomes, the pollen has only 21 chromosomes.
Reason : Pollens are formed after meiosis in pollen mother cell.
Find the odd one out.
Which of the following pairs has haploid structures?
Embryo sac occurs in
Male gametophyte of angiosperms/ monocots is
Draw the diagram of hemianatropous ovule.
An ovule somewhat intermediate in curvature between anatropous and orthotropous is sometimes termed hemitropous or hemianatropous.
_____ ovule turns at a right angle upon the funicle.
Describe hemianatropous ovule.
The Sunflower family has a Campylotropous ovule.
Distinguish champylotropous and anatropous ovule.
Draw the structure of campylotropous ovule.
In pea, the body of the ovule is placed at right angles to the _____.
Anatropous ovule is also called the polygonum type.
